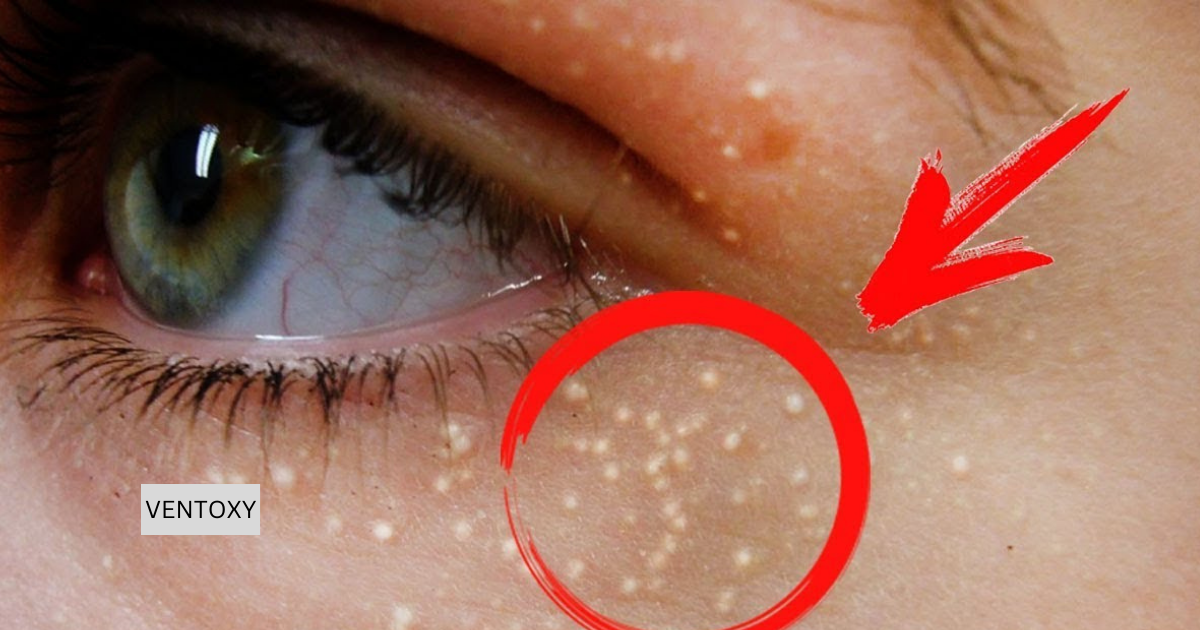
“Miliaria,” often referred to as “heat rash” or “prickly heat,” is a common skin condition that occurs due to blocked sweat ducts and trapped sweat beneath the skin. It’s particularly prevalent in hot and humid climates. The condition can affect individuals of any age but is more commonly seen in infants and young children, owing to their still-developing sweat glands.
Definition and Types
Miliaria is characterized by small, raised bumps on the skin, which can feel itchy or prickly, hence the name “prickly heat.” These bumps may be red or transparent and can cause discomfort. The condition is categorized into several types, each with distinct characteristics:
- Miliaria crystallina: The mildest form, it affects the sweat ducts in the topmost layer of the skin. It’s characterized by clear, fluid-filled blisters and bumps that break easily.
- Miliaria Rubra: Also known as “prickly heat,” this form occurs more profoundly in the outer layer of the skin. Red bumps and itching or prickling sensations characterize it.
- Miliaria Profunda: A less common type affecting the dermis, the deeper layer of the skin. It presents as more significant, harsh, flesh-colored bumps.
Causes and Risk Factors
Miliaria develops when sweat ducts are blocked, and sweat is trapped under the skin. Several factors contribute to this Miliaria blockage:
- High Heat and Humidity: These conditions increase sweating, which can overwhelm the sweat ducts.
- Immature Sweat Ducts: Common in newborns whose sweat ducts are still developing.
- Physical Activity: Intense exercise can induce excessive sweating.
- Overheating: Wearing too much clothing or sleeping under heavy blankets can raise body temperature.
- Certain Creams and Lotions: Some products can block sweat ducts.
- Prolonged Bed Rest: Extended periods of inactivity can increase the risk of developing miliaria.
Symptoms
The symptoms of miliaria vary depending on the type:
- Miliaria crystallina: Clear, fluid-filled blisters and bumps.
- Miliaria Rubra: Red bumps with a prickly or itchy sensation.
- Miliaria Profunda: Large, demanding, flesh-colored bumps, often with no sensation of itching or prickling.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis is usually based on the appearance of the skin and the patient’s recent history of heat exposure or sweating. Treatment focuses on alleviating symptoms and preventing further irritation:
- Cooling the Skin: Use fans, air conditioning, or cool showers.
- Loose Clothing: Wearing lightweight, loose-fitting clothes.
- Avoiding Irritants: Staying away from products that may block pores.
- Calamine Lotion: To soothe itching.
- Hydrocortisone Cream: For more severe itching, though it’s not typically recommended for long-term use.
Complications and When to Seek Medical Attention
While miliaria typically resolves independently without causing serious problems, certain complications can arise, especially if it’s severe or persists for a long time. These complications may include:
- Secondary Infections: Blisters and bumps can lead to secondary bacterial infections if the skin is broken.
- Heat Exhaustion: In severe cases, especially in extreme heat conditions, blocked sweat ducts can impair the body’s ability to cool, leading to heat exhaustion.
It’s essential to seek medical attention if:
- The rash appears to be getting worse or is spreading.
- Symptoms such as fever, chills, or pus from the lesions occur, indicating a possible infection.
- The person affected is an infant or older adult, more vulnerable to complications.
- The rash doesn’t improve after a few days of home treatment.
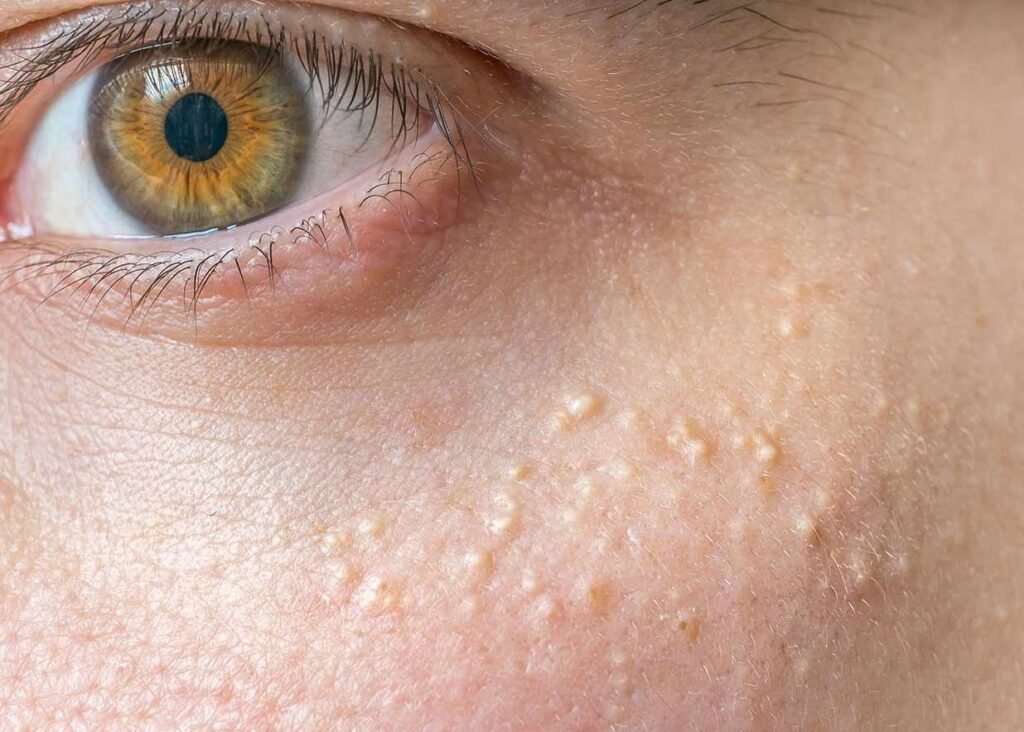
Impact on Quality of Life and Psychological Aspects
Miliaria, particularly the chronic or recurrent forms, can significantly impact the quality of life. The discomfort and itching can disrupt sleep and daily activities and limit participation in social or physical activities, especially in warmer climates. There’s also a psychological aspect, as visible skin conditions can affect self-esteem and social interactions. The psychosocial impact of skin conditions like miliaria is an area that warrants attention. For those with visible skin lesions, there can be feelings of self-consciousness and social anxiety. Healthcare providers need to address these concerns and, if necessary, refer patients to counseling or support groups.
Epidemiology and Demographics
Miliaria affects people of all ages, ethnicities, and genders. However, certain groups are more predisposed:
- Infants: Due to their underdeveloped sweat glands.
- People in Tropical Climates: Due to high humidity and temperatures.
- Bedridden Patients: Especially those with fever or under intense medical care.
- Athletes and Laborers Who are involved in extreme physical activities in hot environments.
Research and Future Directions
Research into miliaria continues, focusing on better understanding the pathophysiology of sweat duct obstruction and exploring more effective prevention and treatment strategies. Innovations in fabric technology for clothing and bedding that allow better heat regulation and sweat evaporation could also play a significant role in prevention.
Cultural and Geographic Considerations
Cultural practices and geographic locations can influence the incidence and management of miliaria. For example, in some cultures, heavy swaddling of infants is common, potentially increasing the risk of heat rash. Conversely, in colder climates, the incidence of miliaria may be lower.
Education and Awareness
Raising awareness about miliaria is crucial, especially in hot and humid regions. Educating the public about the signs, treatment, and, importantly, the preventive measures can help reduce the incidence of this condition. Pediatric care and public health initiatives should include information on appropriate clothing, environmental control, and skin care to minimize the occurrence of miliaria in vulnerable populations.
Lifestyle and Environmental Modifications
Managing miliaria effectively often requires a holistic approach, including lifestyle and environmental modifications. These adaptations are particularly crucial for individuals who live in hot and humid climates or are prone to recurrent episodes of heat rash. Some practical steps include:
- Home and Work Environment: Optimizing air circulation using fans or air conditioners and maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature.
- Clothing Choices: Selecting clothes made from natural fibers like cotton allows the skin to breathe and reduce sweat accumulation.
- Bathing Practices: Taking cool showers or baths can help to soothe irritated skin and remove sweat and oil build-up that could block pores.
- Dietary Considerations: Consume foods and drinks that help to cool the body, such as water-rich fruits and vegetables, and stay well-hydrated.
Miliaria in Different Seasons
While miliaria is most commonly associated with hot weather, it can occur in cooler climates, particularly during seasons when there’s a sudden temperature change. This can happen when individuals dress too warmly or are in heated environments for extended periods.
Global Warming and Increased Incidence
With the ongoing effects of global warming, there’s a potential for increased incidence of miliaria. Rising temperatures and more frequent heatwaves can lead to more cases, especially in regions previously unaffected by extreme heat.
Miliaria in Sports and Physical Training
Athletes and individuals engaged in rigorous physical training are at a higher risk of developing miliaria. Sports medicine now often includes advice on preventing and treating heat-related skin conditions as part of training in hot environments.
Role of Technology and Innovation
Advancements in technology offer new ways to manage and prevent miliaria. Wearable tech that monitors body temperature and humidity can alert individuals to potential risk factors. Additionally, developing advanced breathable fabrics and materials used in sportswear and everyday clothing can help reduce the incidence of heat rash.
The Role of Genetics in Miliaria
There’s ongoing research into the genetic factors that may influence an individual’s susceptibility to miliaria. Understanding these genetic components could lead to more personalized approaches to prevention and treatment.
Prevention
Preventive measures are crucial, especially in hot climates:
- Staying Cool: Seeking shade, using fans or air conditioning.
- Appropriate Clothing: Choosing lightweight, breathable fabrics.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids to maintain hydration.
- Limiting Physical Activity: Avoiding excessive exercise in hot conditions.
Conclusion
Miliaria, or heat rash, is a condition that is intricately linked to environmental factors, lifestyle, and personal health. As our world grapples with changing climates and evolving lifestyles, understanding, preventing, and treating miliaria becomes increasingly significant. From simple lifestyle adjustments to the use of cutting-edge technology and fabrics, there are many ways to manage and prevent this condition. Awareness and education play a crucial role, as does ongoing research into the various aspects of militaria. By addressing this condition’s physical and psychological impacts, individuals can enjoy a better quality of life, regardless of their climate.
READ MORE: WellHealth Organic Vitamin B12: A Comprehensive Guide